Lentigo
What is lentigo?
Lentigo is defined as a small spot on the skin that is pigmented, its edges are clearly defined. This spot is surrounded by normal-appearing skin. It is benign in nature and is due to the overproduction (hyperplasia or increased number) of melanocytes (pigment cells). Owing to their brown-black color, they are also called liver spots. Lentigine is another name for lentigo, contributed by its small, lentil-like appearance.
Are Lentigo and freckles the same thing?
Not quite. Despite both of them have a hyperplasia of melanocytes, only freckles darken with increased sun exposure. Lentigo remains of the same pigment and does not darken, regardless of sun exposure.


What is the difference between Lentigo and Intertrigo?
Intertrigo is the hyperpigmentation of the skin secondary to a fungal infection. Intertrigo, unlike lentigo, causes itching and foul odour.
Does lentigo itch?
No, Lentigo does not itch or cause any symptoms. It is merely a darkening of the skin pigment.
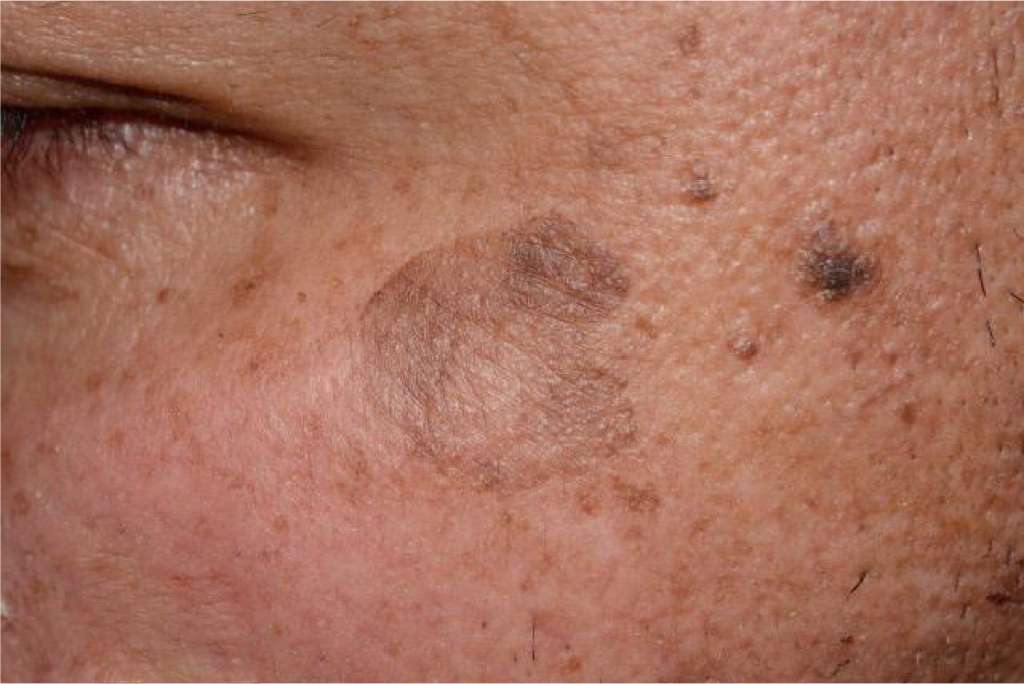
What are the types of Lentigo?
Lentigo (plural: lentigines) is of different types, based on its cause and site of occurrence.
Lentigo simplex
It is the most common type and can be seen congenitally on the trunk, arms, and legs. These spots can, however, disappear with time.
Solar lentigo
It is caused by ultraviolet radiation exposure. Fair skinned people, old people, people who work a lot in the sun, and those who use tanning beds may develop solar lentigo.
Ink spot lentigo
These can be seen in light-skinned people after a sunburn.
PUVA lentigo
PUVA Lentigo starts after psoralen and ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy, which is used to treat skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Tanning bed lentigo
Tanning beds are an artificial way of making skin look nice and tanned despite lack of sun exposure.
Radiation lentigo
Radiation lentigo occurs in areas of skin that have been exposed to radiation – for example, from cancer treatment.
How is lentigo diagnosed?
Since lentigo can be confused with a malignant condition, a doctor will take a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. The sample will be sent to a lab for testing.
Why do I have Lentigo?
Lentigo is mostly linked with increased UV ray exposure. However, if you have a fair complexion or use tanning beds regularly, you are more likely to develop lentigo.
What conditions can cause Lentigo?
Some examples include:
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
- Cowden syndrome
- Noonan syndrome
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Xeroderma pigmentosum
Do women get lentigo more than men?
Lentigo is a gender-neutral skin condition and can occur in almost all ages. However, like most detrimental changes, are evident more in older people. Men and women can equally get lentigo but women are more likely to seek consultation and treatment.
How is lentigo treated?
Bleaching creams, chemical peelers, cryotherapy and laser treatment are some of the options to treat lentigo.
